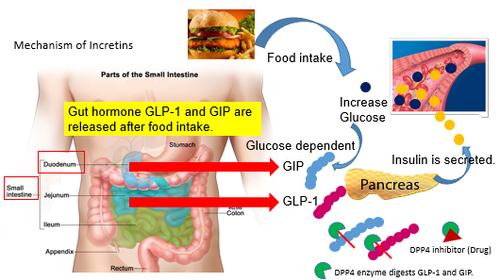
Glucagon is a 29-amino acid peptide that is produced from the cleavage of proglucagon (160 amino acids) by proprotein convertase 2 in pancreatic alpha cells. In intestinal L‐cells, proglucagon is cleaved into glicentin, a 69 amino acid peptide. Glicentin can further be processed into a 37 amino acid peptide oxyntomodulin. These peptides are released simultaneously upon stimulation [2-5]. Glucagon is involved in carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism and is the main catabolic hormone of the body. Glucagon raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and plays an important role in maintaining glucose homeostasis by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Glucagon has traditionally been considered an antagonist to insulin, with insulin reducing blood glucose levels and glucagon increasing them. As the level of blood glucose decreases, the pancreas releases more glucagon. As blood glucose increases, the pancreas releases less glucagon. Once blood glucose levels have normalized, glucagon secretion ceases.
Glucagon also decreases fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissue and the liver and promotes lipolysis in these tissues, which causes them to release fatty acids into circulation where they can be catabolized to generate energy in tissues such as skeletal muscle when required [8]. Glucagon also regulates the rate of glucose production through lipolysis. Glucagon induces lipolysis in humans under conditions of insulin suppression.
Glucagon is secreted from the alpha cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Recent research has demonstrated that glucagon production may also occur outside the pancreas, with the gut being the most likely site of extrapancreatic glucagon synthesis [10]. IVD Glucagon in diabetics has been found elevated absolutely or relatively to insulin, and it has been proposed that glucagon contributes to the development of hyper- and hypoglycemia [11-15]. Researchers have found that patients with diabetes are more likely to develop pancreatitis.
The Glucagon ELISA is a two-step capture or ‘sandwich’ type immunoassay. The assay makes use of two highly specific monoclonal antibodies: A monoclonal antibody specific for glucagon is immobilized onto the microplate and another monoclonal antibody specific for a different epitope of glucagon is conjugated to horse radish peroxidase (HRP conjugate).
For the quantitative measurement of Glucagon in human EDTA plasma by an ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay). 510(k) Exempt - For in vitro diagnostic use only.
- Assay Description:
- 60 min (RT) + 30 min (RT) + 15 min. (RT) = 1 hour 45 min total incubation time
- Catalog number:
- IB59142
- Configuration:
- 96 Determinations, 12x8 removable strips
- Controls:
- 2 controls. lyophilized
- Design:
- Enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) technique
- FDA Status:
- 510(k) exempt - IVD
- Protocol:
- Notes:
- The protocol for this product (see above) is intended to serve as an example only. Please refer to the Instructions For Use provided with the assay kit for precise details.
- MSDS:
- Available Upon Request
- Sample Types:
- EDTA plasma
- Sample Volume:
- 100 μL
- Standards:
- 7 standards, prepared from lyophilized stock
- Standard Range:
- 0 / 11 - 352 pg/mL
- Sensitivity:
- 5.33 pg/mL
- Storage:
- 2 - 8 °C
- Species:
- Human